Activity plan:
According to the Ethical Guidelines for Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence, there are seven requirements that AI systems need to meet. The theme of our activity is the sixth requirement and this is a requirement for the well-being of society and the environment that includes sustainability and benefits for the environment, social impact, society and democracy. Artificial intelligence gives us the ability to question the status quo and decide what kind of present and future we want for ourselves and others.
The activity covers the following objectives of learning, skills and competences:
- introduce students to artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms;
- understand the expansion of human skills and decision opportunities in combination with AI systems;
- discover the role of AI in creating digital images using simple tools for creativity;
- create a drawing related to sustainable development (e.g.: "green" technologies, climate change, environment, sustainable cities and communities...) with the help of an Autodraw (https://www.autodraw.com/ ) app on a computer, tablet or smartphone
- Generate a photo of your city's landmarks or an avatar used in the project or a photo of one of the activities in which students participated during the duration of this project using the Deep Dream Generator (https://deepdreamgenerator.com/) application
- Create a photo of the landscape using the GAN neural network with the Artbreeder application (https://www.artbreeder.com /)
- Answer the questions you've asked with each activity.
- attach answers, pictures and photos to the padlet wall
- students can work independently, in pairs (2 students) or in groups (up to 4 students). Groups can be made up of students from the same school or from different schools. In the shared List of participants of the 10th activity, each student will record the selected mode.
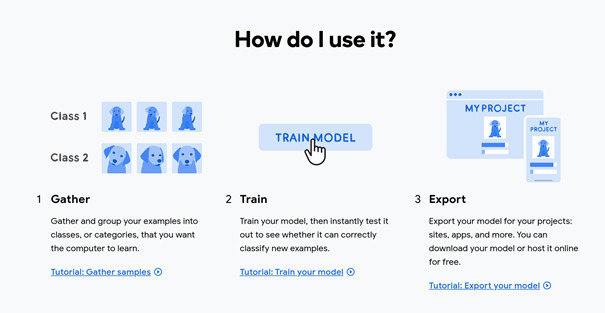
- for students who want to know more: An activity has been created with the help of Google Teachable Machine through which they will learn about machine learning
Through this activity, we will develop technology usage skills, understand the role of new technologies, practice digital skills on mobile devices, and explore aesthetic dimensions with digital tools.
Contrary to popular belief, artificial intelligence is not intelligent machines capable of thinking like humans but applying sophisticated algorithms to huge data sets, using strong computing power, which among other applications allows for unexpected insights, pattern recognition or computer vision. It's not the technology of the future. It is already shaping our digital world: identifying people on imaging systems (video surveillance, automated recognition on social networks); deciding what you see online, automating content on social networks; recommendation mechanisms on websites with videos or online stores; launching voice recognition technologies on mobile devices; optimization of traffic and routes on folders and sharing transportation; categorization, automatic response, filtering suggested text and spam to e-mail, and the like.
For starters, watch the video Recording Introduction to Artificial Intelligence in the Classroom that will introduce you to the topic and activities that we will engage in. (Source: Europe Code Week; Introduction to Artificial Intelligence in the classroom by Artur Coelho and Marjana Prifti Skenduli).
Estimated time period:
Provided online tools:
- Task You Sketch - AI draws
Access the Autodraw (https://www.autodraw.com/) app on your computer, tablet, or smartphone. Use the app to sketch shapes: sketch in an empty area (or fill it with any color). The algorithm will begin to generate suggested shapes as you draw: the top ribbon will begin to interactively suggest shapes. Choose from suggestions for creating drawings, using several shapes, colors and backgrounds. The theme of your drawing should be related to sustainable development (for example: "green" technologies, climate change, the environment, sustainable cities and communities...)
At the end of the activity, reply:
How could AI guess shapes based on simple drawings?
Was it creative? How did AI learn?
Could you create a better, more interesting design independently or with the help of AI?
How can AI understand what you want to draw?
Additional clarification: This app shows us how AI systems understand data and make decisions based on inputs. It's all about pattern recognition. The algorithm is trained using a wide set of forms. And the training never ends and the algorithm itself amplifies its learning with user input. By selecting an image from a suggestion, the algorithm learns how to better understand unsafe forms.
You can find a snapshot of the procedure on the screen at this link.
Example:

Place your photo and replies on the padlet wall in the Activity 1 You sketch - AI draw column
2. Task Dream like a machine
Sign in to the Deep Dream Generator (https://deepdreamgenerator.com/) app. Click the "Generate" button, upload a photo of your city's landmark or the avatar you use in our project, or a photo of one of the activities you have participated in during the duration of this project, and select the Deep Dream option. In the settings, select "Keep it private" and click the "Generate" button. It may take several seconds to generate the image. Check the results, and then select Go Deeper to set several settings, or choose different types of Deep Dream algorithms (Deep Dream, Neuron, or Valyrian). Repeat until you are satisfied with the results. Store your newly created photo.
At the end of the activity, answer the question:
What's goin' on? Why does AI turn a photo into a surreal image?
Additional clarification: Image recognition algorithms, such as facial recognition or shape recognition, should be trained with image strings to learn how to analyze, understand and extrapolate the result. The scope of these systems shall be limited by the datasets on which they are trained. For example, image recognition algorithms are known for their vulnerability to unintentional racial profiling and false positives. But the Deep Dream algorithms do something a little different: they interpret what they "see" on the input of the image, based on the types of shapes on which they are trained, not describing what is in the picture, but what they think is an image.
You can find a snapshot of the procedure on the screen at this link.
Example:

Place your photo and response on the padlet wall in the Activity 2 Dream like a machine column
3. Task Create machine visions with parental image and genes
Sign in to the Artbreeder online app (https://www.artbreeder.com/) , select Create (located in the upper right corner and has a +)" Then on the Image tab, select Landscape. The app will produce a few images at random. On the +Genes tab, explore the genes offered in several categories and choose what gets your attention. Genes are images from sets in which the algorithm is trained, used to remix and generate new images. Click "Add parent" to add more genes. Check the results. Notice that with more genes added, GAN generates new images by mixing visual elements.

For each new gene, you have sliders to set the percentage of each gene in the suggested composition. Select the image between images generated by AI. When you're happy with the result, click the download button to store the picture.

Additional ojourage: the algorithm generated random images, which were mixed with genes, generated new real-time results using GAN AI, which in all steps tried to guess the user's preferences, based on their input. Store your newly created and selected photo.
At the end of the activity, answer the questions:
Who was the creator of the final painting? AI? You? Both?
How does my computer create these images?
Additional clarification: GAN neural networks can be trained using image sets, so they can extrapolate new data later. The technique places two algorithms opposite each other: one generates new data, based on user inputs and training sets, and the other judges the output data to better suit the intentions of the user. These algorithms can be used to generate new images, remix existing images in unexpected ways or, if a work of art is used as a set of training data, to understand its aesthetic structure, to give deeper knowledge to artists and art historians, or to apply the artist's personal style for new types of paintings.
You can find a snapshot of the procedure on the screen at this link.
Example:

Place your photo and response on the padlet wall in the Activity 3 Creating machine visions column with the help of parental image and genes
For those who want to know more:
This part of the activity refers to the basic concepts of machine learning and the task of classification. With machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI), we will create a classifier of fruit images. To create ml models we will use Google Teachable Machine. To get started, collect and group examples of images of the category that you want the machine to classify. Na Teachable Machine, select Start/Get Started, and then select "Image Project/Image Project." Create at least four different classes or categories of which the computer will feed on examples and train to identify and classify different varieties of fruits, name the examples of the classes: "Apple", "Banana", "Orange" and "No fruit". Work out the "Training Data Set" and capture samples of the images that best represent each class (you can keep the first class of fruit, for example, an apple, in front of a webcam, a clique on "Webcam/Webcam", and then "Keep for recording/Hold to record " while moving the fruit in different angles. Repeat the procedure for the remaining fruits / classes. Take at least 25 images for each class of subject. Be careful where you take picture samples for the "No Fruit" class, be sure to change the background and record your hand without fruit. Once all classes are ready, you can click on "Train/Training" and in Preview/Preview believe that the model works (the "Test Data Set" must be available to you as an assortment of different fruits, different from those used to teach the classifier or other fruit basket). To perpleate whether the model is working correctly and evaluate its performance, study the cases when the model is not working properly (for example, keep two apples at the same time, raise the printed image of the banana...). Through this activity, participants will get to know the basic concepts of AI and ML, understand the task of classification in the context of supervised machine learning and basic material parts of the classification channel, create and fine-tune the classifier and recognize the importance of the quality and quantity of training data and their impact on the accuracy and fairness of the classifier.