Olina Tsoraklidou-Sofia Tsoraklidou,Anastasia-Maria Perperidou- Evaggelia Passia |
November 2016
In General
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the perceptible shaking of the surface of the Earth, resulting from the sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can be violent enough to toss people around and destroy whole cities. The seismicity or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time. Earthquakes are measured using observations from seismometers. The moment magnitude is the most common scale on which earthquakes larger than approximately 5 are reported for the entire globe. The more numerous earthquakes smaller than magnitude 5 reported by national seismological observatories are measured mostly on the local magnitude scale, also referred to as the Richter magnitude scale.
Earthquakes in Greece/
The high seismic activity of the country is due to the fact that it is located at the boundary of the Africa-Eurasia convergence. Within this framework, the Anatolian plate rotates counterclockwise (fig. 1). From the west, the Adria microplate rotates counterclockwise. As a consequence, the Aegean microplate moves fast towards SW. The external Aegean area is subject to a general compressional stress field and the inner Aegean area experiences a general extensional stress field.
Greece often hosts large magnitude earthquakes, whilst a moderate or small magnitude earthquake is felt every 2-3 days on average (fig. 2). Although the majority of these earthquakes are shallow, a few cases have been recorded as «devastating» for the human environment or for life loss (e.g., the 1881 Chios, 1953 Cefallonia, 1999 Athens earthquakes). No historical information is provided for extensive migration of populations and obliteration of civilizations in Greece due to earthquakes.
Earthquake types
- Volcanic earthquakes
- Tectonic earthquakes
- Rupture dynamics
- Tidal forces
- Earthquake clusters
- Aftershocks
- Earthquake swarms
Resources
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Earthquake
- http://www.geophysics.geol.uoa.gr/papers/makro/makro205.p
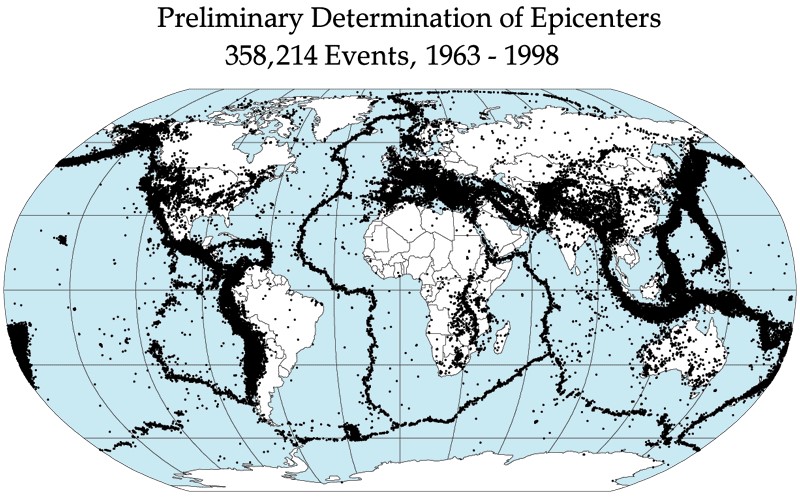
https://el.wikipedia.org/wiki/%CE%A3%CE%B5%CE%B9%CF%83%CE%BC%CF%8C%CF%82#/media/File:Quake_epicenters_1963-98.png
Earthquakes
Can we predict them?
- The analysation of the electric seismic signals at regional level can help in identifying an very large upcoming earthquake, until two months before it happens, according to a new study of Greek and Japanese scientists, involving the Greek science scientists Nik. Sarlis, Euth. Skorda και Pan. Barotsou of the team ΒΑΝ. The study gives new options seismic's prediction.
- The researchers, with first author of the study Nikolas Sarlis, divorced Japan, a country where earthquakes are very common in small areas and reviewed for each region of the pre-earthquake electrical signals, which are recorded where six very strong surface earthquakes size above 7.6 degrees. Earthquakes are occurring during the period 1984 - 2011 and among these was the devastating earthquake of nine degrees, which caused a massive tsunami and the Fukushima nuclear accident.
- Already in the previous studies (and in PNAS 2013) Greek and Japanese scientists have identified, throughout the Japanese territory, that variations of a seismic parameter (K1), a new time domain called "natural time", reach at a minimum price a few months before large earthquakes.
- The new study goes a step further, showing that the same variation of the parameter K1 reach their minimum value almost simultaneously (within two days) so throughout Japan, and in those small areas that are closer than a few hundred kilometers from the epicenter of the earthquake forthcoming.
- This finding, according to scientists, gives new possibilities seismic forecasting, particularly as regards the likely future epicenter of a strong earthquake. However, the forecast for the geographical area where probably the earthquake happened, includes a sizable geographical area of hundreds of kilometers.
- Professor Panayotis Varotsos (known together with Alexopoulos and Law, from the initial creation of earthquake prediction method with the acronym BAN) and younger colleagues Nikolas Sarlis and Efthimios garlic, belonging to the Department of Physics Department of Physics University of Athens, where the 1995 Pan. Varotsos directs the Institute of Physics of the Earth's crust. The Japanese researchers Toshiyasu Nagao, Masashi Kamogawa, and and Seiya Uyeda from Japanese universities and the Academy of Sciences of Tokyo.
- Since 1984 was introduced, the method uses VAN electric seismic signals (SES) within the Earth for the possible provision of an earthquake. From then until now, the method of studying these signals has attracted the interest of the international scientific community.
- For years, Japanese researchers have applied the methodology of the natural time and electric seismic signals, resulting, according to the Greek scientist at comparable results regarding predictability, as those that have arisen from the respective analyzes earthquakes in Greece.
- As told the Athens News Agency Panayiotis Varotsos, "a large earthquake, although many usually ask for the location of the epicenter, which is just the point where we believe that the breakage starts, what eventually happens is that ruptures a extensive area has hundreds of kilometers long. We, the natural time method, we detect a signal pre-earthquake a few months before the earthquake, and then determine both the future epicentral area, and the time it happens, approaching him with a few days precisely. We continue our research efforts despite the difficulties. Every day we learn something more. "
Source: http://www.protothema.gr/environment/article/438553/meleti-enas-megalos-seismos-borei-na-provlefthei-eos-kai-duo-mines-prin/
The big earthquake of Thessaloniki.
Deadly earthquake, which occurred at 23:04 of June 20, 1978 centered between Lake St. Basil and Volvi and shook northern Greece. Magnitude 6.5 on the Richter scale and intensity of 8-9 degrees on the Mercalli Intensity Scale, was the first major earthquake that affected a modern Greek city, with great economic and social consequences. Apart from the city of Thessaloniki, great damage was caused in the prefectures of Thessaloniki, Kilkis, Serres and Chalkidiki.
After the event of the earthquake and panic prevailed unprecedented chaos in Thessaloniki, since all the residents have fled their homes and were trying by any means to leave the city. Telephone communications and electricity were discontinued in many areas of Thessaloniki. That night in Thessaloniki, the state machine had "misfiring" and the emergency plan "Xenocrates" was a dead letter.
In Thessaloniki, an eight-storey apartment building in the Hippodrome Square collapsed, leading to the deaths of 29 of the tenants of. Other 20 people were killed, bringing the total number of victims of the earthquake of June 20 to reach 49. The injured totaled 220. The damage exceeded one billion euros at current prices. 9.480 buildings suffered irreparable damage (3170 in Thessaloniki, including 35 schools), 23 589 serious injuries (13 918) 67 541 and lighter (49 071 in Thessaloniki). Significant damage suffered and Byzantine monuments, which were maintained by the liberation of Thessaloniki in 1912.
The earthquake was felt in many parts of Greece and Bulgaria, southern Yugoslavia and Albania. The main earthquake was preceded by a large number of pre-earthquake, the largest of which took place on May 23 (23:34, 5.8 R), followed by aftershocks, the largest of which took place on July 4 (22:24, 5.1 R).
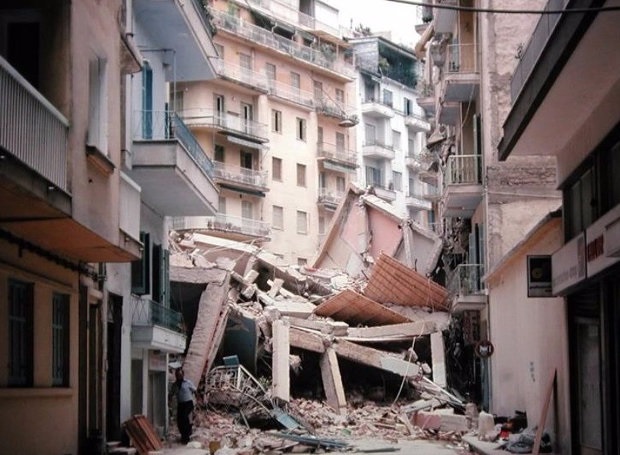

Immediately after the earthquake, the state is awakened and made strenuous efforts to heal the wounds. Material losses were restored relatively quickly into and from the special tax imposed by the government of Constantine Karamanlis. Help earthquake victims took over the newly established "Earthquake Rehabilitation Service of Northern Greece" (YASVE), which became the model for subsequent Earthquake Rehabilitation Service. The Konstantinos Karamanlis himself had to spend three days in Thessaloniki to dispel rumors that spoke of new earthquakes.
On the occasion of the earthquake of Thessaloniki and later of Athens (1981), founded in 1983, EPPO (Earthquake Planning and Protection), which is the competent body of the state for the design of earthquake policy of the country.
Source: https://www.sansimera.gr/articles/940
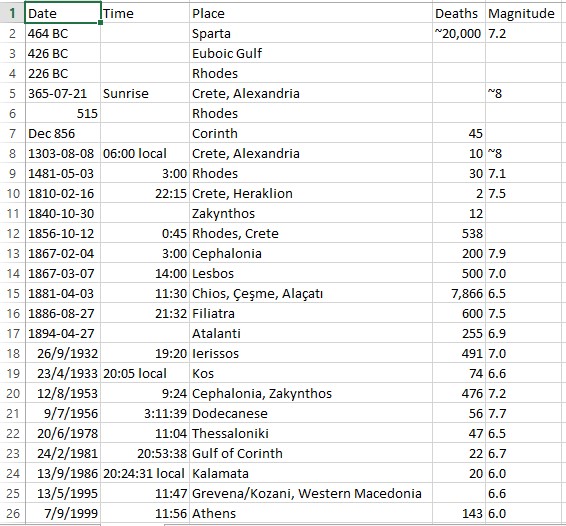
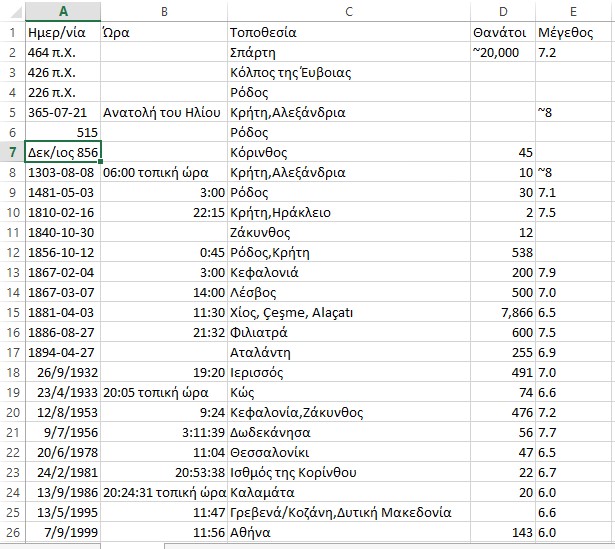
Earthquakes in our area from 426 BC until today.
Earthquakes from antiquity even been the subject of interest and wonder for humans. Usually they considered supernatural phenomena that cause fear and panic and were accompanied by a host of superstitions and prejudices. No other natural phenomenon not caused awe and panic at the same time mainly due to the fact that usually occurs suddenly and without warning while there react.
The earthquake is a natural phenomenon - inextricably linked with the history of the earth. In the long history of our country we have recorded many earthquakes. The Greece ranks first in terms of seismicity in Europe and the sixth worldwide. It should not seem strange that the earthquakes in our country are made with great frequency and intensity and we must all realize that we are an integral part of our lives.
Prior to 426 p. X. Information about earthquakes in our region we have identified. After that year, the main recorded seismic events of the wider region are below. According to sources always ancient texts and historical. And Professor of Geology AUTH Mr. Papazachos, Earthquakes of Greece 2003.
1. The year 426 p. X., In Winter, the ancient people lived one of the most devastating earthquakes shook the region of Fthiotida, which was felt in Athens, even causing displacement and the southeastern part of the Parthenon just 12 years before he had finished, Euboea, Thebes and most of all the Boeotian Orchomenus. The strength of the earthquake was 7.0 on the Richter scale, and was centered Skarfia. (Thuc. C., 87-89) and Papazachos for potency.
Strabo describes the consequences of this terrible earthquake as follows. The hot springs of Edipsos Thermopylae dried up for three days. Orei (Evia) collapsed seven hundred houses and seaside wall. The Skarfia destroyed fundamentally, seventeen hundred people were killed, while in Thronio about nine hundred. Disasters were in Echinos in Falares Iraklia, Lamia and Larissa. The wall of Elateias cracked and Atalanta created rift. A trireme sprang from the dockyards and fell over the wall.
2. The year 347 p. X., Earthquake force 6.0, on the Richter scale, centered Delphi. According to testimony by Diodorus when Falaikos was quarterback of Phoceans and preparing soldiers to dig around the tripod at Delphi to find the treasures of the temple of Apollo, they were major earthquakes that terrorized the Phocians. This was seen as a clear sign that the gods would punish the sacrilegious. So I stopped the works. Strabo mentions the same but reflects the fact that the era of General Phoceans was Onomarchus, that a few years earlier (-355 p. X.) (Georgiades 1904, Guidoboni et al. 1994).
3. The year 279 p. X., Earthquake force 6.4 on the Richter scale, centered Delphi. According to testimonies of Justin, Pausanias and Appian during the invasion of Vrennou and the army of the Gauls in the Parnassos region of the mountain he was torn by an earthquake and fell into Gaul army. Terrible rain of sharp stones slumped between them causing damage.
The whole area occupied by the army of the Gauls vibrated violently during most of the day (Hoff 1840, Georgiadis 1904, Guidoboni et al.1994).
4. The year 226 p. X., Earthquake 6.4 on the Richter scale, centered on Tithorea, which caused it and crack. B. Papazachos, Earthquakes of Greece 2003.
The earthquake that struck the ancient Kitinion (current Palaiochori Dorians of Fthiotida).
And attested by an inscription found at Xanthus of Lydia, contained a letter from the Dorians of Kytiniou (leading city of ancient Doris existing on the northern slopes of Mount Parnassus), which mentioned earthquake and seek financial support from their blood brothers in Xanthos .
They write that at that time, that Antigonus invaded Phocis, part of the walls of all the cities in the region collapsed by earthquakes and young men ran for help to the oracle of Apollo at Delphi.
It is likely this earthquake to be part of a wider outbreak, including the earthquakes that destroyed the walls of Melitaia (located on the north side of Othrios) for which the King of Athamanon gave ten pieces of silver talents to rebuild these walls.
It is also possible earthquakes of the same wider outbreak linked to a drop in the sea of Larymna region. For her, Polybius says that when Antigonus (son of Demetrius) sailing to Larymna held unusual retreat of the sea, so that the ships were to land (Bousquet 1988, Guidoboni et al. 1994).
5. In the year 105 or 106 m. C .: Destruction of Broth (today Atalanta) and Oreos in North. Gujarat. The strength of the earthquake was 6.4 on the Richter scale. Eusebius Papazachos, 2003. Earthquakes of Greece Papaioannou 1994, Guidoboni et al. 1994

6. The year 361. AD., Earthquake 6.8 on the Richter scale, centered Delphi. For the earthquake we have information of Affection who writes that Oribasius, who had been sent by the Emperor Julian Delphi to receive oracle says nice palace was destroyed.
It is no longer true that Apollo has a home and a laurel bush for oracles and a lalousa source. Even lalon water has dried up.
There is an inscription from Nafplion who says that the city xanasikose head when Emperor secured protection from earthquakes and maritime disasters in the basilica and other buildings.
In another description, from Corinth, it states that restoration work was carried out by the Emperor Flavius Valentinian. Archaeological excavations in Corinth and Nafpaktos revealed additional evidence for this earthquake (Guidoboni et al.1994).
7. In the year 375. AD., A great earthquake which devastated the Greek provinces and suffered heavy damage large parts of continental and northern Greece (Zosimas IV, 18, 2 V, 6, 5). Meanwhile, of course, they made and other earthquakes, are not mentioned.
8. From the year 513-570. AD., The Byzantine Empire became terrible earthquakes.
9. The year 551 7th or July 9th. AD., And according to July Smitio became terrible earthquake, whose disasters were horrible especially in despite Krisaiko Bay locations (Itea Gulf) and in Viotia and shores of Maliakos Gulf.
From this terrible earthquake destroyed many villages and eight cities, including Chaeronea, Patras and Nafpaktos.
Many places were faults, but not closed immediately and others remained open it difficult to transport.
Despite the Maliakos bay or sea entered depth in adjacent cities of Echinos and Skarfia where and destroyed killing many inhabitants.
He remained not the sea for some time to the earth's surface. When he left he left monstrous fish, when came into contact with fire altered their bodies and pus was running!
The fact that the notes and the Procopius of Caesarea. Since not affected by the earthquake towns and villages killed several thousand people. 'Vestments not the passages that, th public schism onomastai and earthquake oversized epipeson Pleiades phonon people or any of the other Hellenic eirgasato even speak feast on. celebrates gar received from all of Greece hereby then due syneilegmenoi many "(prov. rCT. Paul. D. ch. 25 fin. Evagr. D. '23. Seibel de gross Past zur Zeit Justinians I, pp. 16 and following). According to the professor. Papazachos power of this earthquake was 7 degrees on the Richter scale.

- The year 996. AD., Was devastating earthquake in Galaxidi and the surrounding area (Chronicle Galaxidi ibid).
11. The year 1323 m. X., Became bigger and deinoteros earthquake of the 996. In which the historian of the time of the fall of Constantinople George Sphrantzes (1401-1480) described as "the pammegiston" because Greece resulted in major disasters .
12. The year 1343. AD., The other in B. Greece, earthquake and himself in tension with the 1323, and that he made the same disasters and near destroyed all the cities of Thrace.
13. The year 1509 m. X., Another strong earthquake shook the place (Chronicle Galaxidi ibid).
14. The year 1545 m. X., On March 24 was very strong earthquake measuring 6.8 on the Richter scale with epicenter Lamia and had 4000 victims. 1545,
According to Ambraseys (1994) there are two texts of Western origin, referred to in this earthquake, which were written immediately after the earthquake.
The first text is a letter which was sent from Corfu to Vienna, stated that on March 23, 1545, three hours before dawn, was a terrible earthquake that destroyed the Lamia (Sittuni), where about 3700 corpses were recovered from the ruins and others remained under the rubble.
The High (Nonaptre) vlaftike less from Lamia, but two-thirds of this city destroyed and killed many people.
There, the earth opened and a stream of water poured in the region of Lamia.
The tops of two mountains collapsed due to the storm and earthquake. The walls of Nafpaktos (Lepanto) rigmatothikan into two parts by the earthquake.
The quake was strongly felt and lasting in Zakynthos and Kefalonia and felt in Corfu.
The second text, whose source is news from traders of Lepanto, says that two successive earthquakes took place, which completely destroyed the High, Lamia and Gardiki (Pelasgia), which caused many casualties.
Lesions at Lepanto were insignificant except for the collapse of the wall section, which was already tottering. The text does not state the date of the earthquake, but only that he was in 1545.
In a manuscript of the monastery Olympiotissa (Elassona area) of the year 1577 indicated that there was a great earthquake in Greece and destroyed Lamia (ask), the High (New Patras) and Nafpaktos.
They fell and the walls of these cities (Skouvaras 1967, Schreiner 1975, Papaioannou 1993c).
Another manuscript is in the National Library of Athens, (derived from the monastery Prousou or when Alexander comes from the monastery Dushan) and drafted in 1592/3) that the earthquake destroyed most of Lamia, many people were killed, vlaftike whole Greece and Wallachia and the vibrations lasted several days Greece and Wallachia and the vibrations lasted several days (Lambros 1910).
In a remembrance of the cloister of Kafsokalyvia Mount Athos is written that in 1544, when martyred in Thessaloniki, the martyr Michael from Granitsa Agrafa became earthquake in requesting (Sophianos 1979-1980) and in remembrance of Vatopedi Monastery of the year 1584 indicated that 1544 sank request (Kadas 2000).
From the Greek texts is not clear the exact genesis date of this earthquake has been confusion between it and the earthquake in northern Thessaly held on April 24, 1544.
This is because these Greek texts were written several decades after this great earthquake Valley Sperchios and him who was about a year earlier in northern Thessaly.
This is probably for two different earthquakes. This follows from
referred to above, based on detailed information recently published (Alexandropoulos 1994, Alexander 1999) and from seismotectonic knowledge.
15. The year 1544, m. X., April 22 was very strong earthquake measuring 6.8 on the Richter scale with epicenter again Lamia. According to the professor. Papazachos, Earthquakes of Greece 2003.
16. The year 1580. AD., An earthquake measuring 6.8 on the Richter scale, brought about great upheavals and disasters in Galaxidi, Amfissa, Nafpaktos, Lidoriki and all neighboring countries and to the Ionian islands 3 dead (Chronicle of Galaxidi ibid).
17. The year 1660 m. X., Another devastating earthquake measuring 6.4 on the Richter scale took place in the region, focusing Galaxidi. Dead 5 (Chronicle Galaxidi ibid).
18. The year 1740 m. X., On 4 October earthquake measuring 6.6 on the Richter scale with epicenter Thermopylae brought terrible disasters and the deaths of 10 people.
In narration browser Pocoque stated that when he came to ask (Lamia), which was then 300-400 houses, an earthquake occurred at night on 23 September.
All Greek houses, which were constructed with mud, collapsed and
They killed some people.
No Turkish houses collapsed because they were made with plaster.
Destroyed the neighboring villages (Thermopylae, Molo. Renginio. Palaiopatra (High). Since the earthquake collapsed the Monastery Agathonos near High.
Cracks six inch width observed in the plain. According remembrance was written in the monastery of Zagora Archangels, the earthquake was large and roar and areas of Evia and Lamia threw many houses and
churches and demolished villages.
According to another remembrance of the monastery Barlaam Meteora the quake was strongly felt in Zagora. The quake was strongly felt even in Ioannina. (Konstantinidis 1939. Simopoulos 1973 Veis 1984 1993 Papaioannou, Ambraseys and Jackson 1997).
19. The year 1754 m. Ch. June 15 high intensity 7 earthquake on the Richter scale and centered Nafpaktos brought tromaktikotates disasters together and killed 20 people.
20. The year 1758 m. Ch. May. Earthquake centered Lamia, eliminated three islands near Evia. also caused the collapse and disappear beneath the waves of a part of the Pontikoniso, located in the northern part of Evia. The strength of the earthquake was 6.8 on the Richter scale. According to the professor. Papazachos, Earthquakes of Greece 2003.
21. The year 1852 m. Ch. July 14 The earthquake measuring 6 on the Richter scale, caused collapses of rocks near Delphi and the area between the Gravias and Mavrolithari destroyed many villages where there were 10 casualties and killed several goats from collapse rocks.
It was felt in Zakynthos (Schmidt 1879, Ambraseys and Jackson 1997).
22. The year 1853. AD. August 18 and September 29 in the region of Thebes was an earthquake measuring 6.4 on the Richter scale with very large disasters in Atalanti cities and Chalkida and 11 casualties. According to the professor. Papazachos, Earthquakes of Greece 2003.
23. The year 1870. AD. August 1, had devastating intensity earthquake of 6.8 degrees on the Richter scale, in Upper Souvala in Amfissa with 117 casualties, landslides, cracks and other damage.
24. The year 1870 m. X., 19 to 20 July at 2 40 morning another big quake was Fokis lasting three and a half years that the aftershocks reached the number of seventy thousand (70,000), of which 300 were strong . Major disasters suffered Chrisso, Delphi, Amfissa, Itea and other such villages. The surface seisthike then estimated at 2375 square kilometers, and all had centered on the valley of Amfissa. The duration of these earthquakes was the longest time at all they had done until then.
25. The year 1894. AD., In Locris were two destructive Tectonic earthquakes on the same fault Atalante, that the rift broke into two pieces. The first earthquake that took place on April 8 at 4 p. M., With a magnitude of 6.7 on the Richter scale and broke the piece of Larymna to the village worship.
The earthquake caused major damage and many burglaries: a) along the Skala, b) between Pefkohori and Malesinas c) Between Martin - Atalanta and d) In Farmakorefma between Lebanon and Skenteraga.
This earthquake load by tectonic trends neighboring piece of fault (from worship to Atalanta) which broke on April 27, 1894 by an earthquake of 6.9 degrees on the Richter scale. The new powerful vibration has many secondary effects (destruction of caves, drying or genesis of new sources, landslides, tidal waves, etc.). Display the fault of Locris 55 km in length that reaches the Lamia and secondary sectors. Final account of earthquakes April 1894: Victims = 255 dead, 146 seriously injured Damage = Crashing 3.783 houses.
So far the rift Atalante has not given ... "signs of life". Focusing both earthquakes were the Evian Gulf. The victims of this earthquake was 255 people. Proceedings colloquium-natura Sperchios - Soft - 04 123
The fault of the Atalante studied by Pantosti et al. (2004). The team dug three trenches perpendicular to the fault line near the town of Atalanti and found evidence for three earthquakes. A large earthquake occurred between 50 p. X - 230. AD, another during the Middle Ages (770-1160 m. X) and the last in 1894. This means that the period of repetition of large earthquakes is between 540-1120 years .
26. The year 1916. AD. September 27: A strong earthquake of 5.9 degrees on the Richter scale causes damage to Lihada. Proceedings colloquium-natura Sperchios - Soft - 04 123
27. The year 1965 m. X., On July 6, Enceladus Phocis hit 6.3 on the Richter scale and had one dead
28. The year 1974 m. X., November 14, 1974: Earthquakes 5.1-5.2 on the Richter scale. Focus Maliakos. Proceedings colloquium-natura Sperchios - Soft - 04 123
29. The year 1975 m. Ch. April 1, 1975: An earthquake of 4.5 degrees on the Richter scale and causing damage to Haliartus. Proceedings colloquium-natura Sperchios - Soft - 04 123
30. The year 1979 m. Ch. 2 Dekemvriou1979: Seismic vibration 3.8 on the Richter scale. Maliakos Proceedings colloquium-natura Sperchios - Soft - 04 123
"In particular for the fault zone Atalante geologists Pavlidis etc. (2004) report that the maximum expected earthquake size is 6.8 Richter with probability generating <4 50 = "" br = ""> this earthquake is higher in the order of 1000 (maybe 2000) years. "
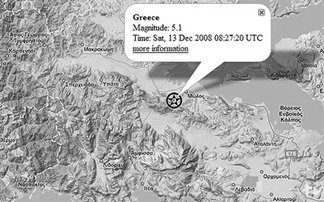
31. The year 2008. AD. December 13, 2008, a strong earthquake of 5.1 magnitude vibration on the Richter scale was felt in Athens shortly after half past ten a.m..
The epicenter of the earthquake was located 138 kilometers North- west of Athens in the region Amfiklia in Fthiotida (50 km southeast of Lamia).
The quake had a focal depth of 10 km and was felt notably in several regions of Fthiotida, Viotia, Attica and Evia.
Left: On the map the epicenter.
A stone house collapsed, while the church and another approximately 20 houses damaged. That is so far account the checks carried out by the engineers of prefecture morning. Because the quake dislodged rocks on the road between the highway and the village Mendenitsa thus stop traffic. The news media of the time.
32. The year 2009 m. Ch. 3 August. Weak earthquake 3.6 magnitude vibration on the Richter scale at a depth of two kilometers occurred shortly after 3 am Tuesday in Fthiotida. The epicenter of the earthquake was located in the area of Thermopylae and was felt in the region of Locris. There are no reports of damage. The news media of the time.
Source: http://el-vima.blogspot.com/2014/02/426.html
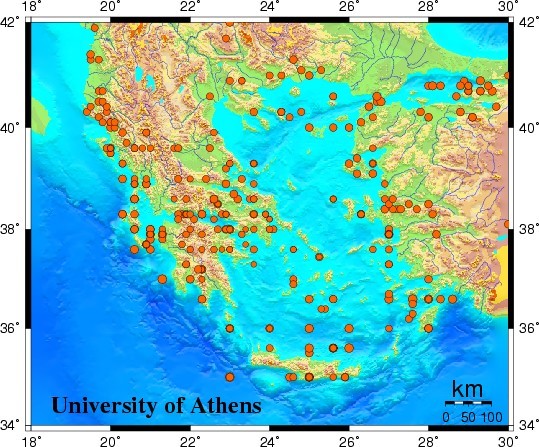
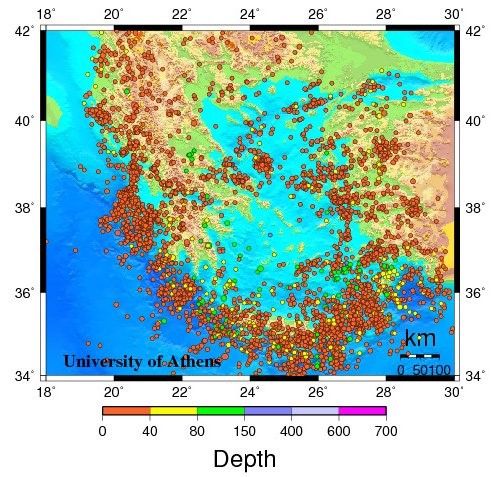
Seismicity in Greece
600 BC - 1899
1900 - 1963
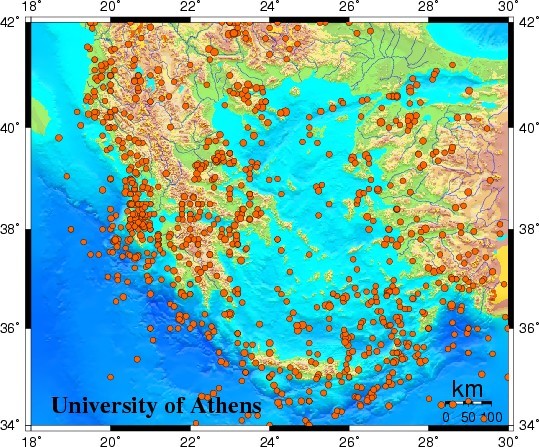
1964 - 1999
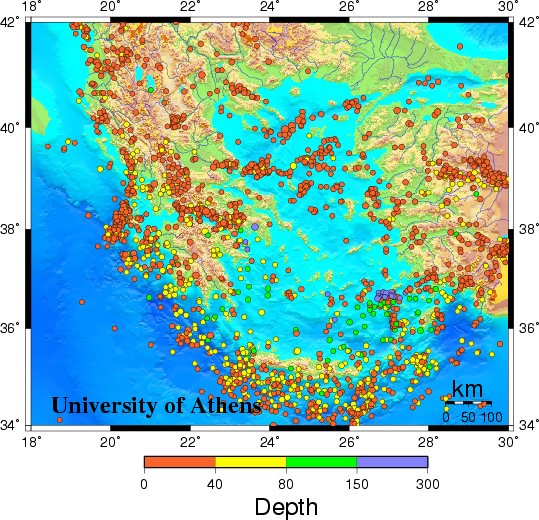
2000 - 2008
Historical earthquakes that struck Thessaloniki
Assiros,Thessaloniki 1902
Earthquake measuring 7.9 on the Richter scale struck on August 11, 1902 the area of Assiros in Thessaloniki.
Five people were killed.The damage to brick buildings was big,especially in Assiros as well as in Langada and in Agios Vasilios.In Thessaloniki many buildings had problems as well as the port, but only few of them had serious damages.The largest of the cracks observed in the soil had length 100m.
Athos,Chalkidiki 1905
In november 1905 a 7,5 Richter scale earthquake hit the Mt. Athos Peninsula. The epic centre was located near the monastery of Stavronikita as to be seen on this map.There was damage in Karyes, Lavra, Kavsokalivia and many other places. The earthquake caused also a huge stone avalanche on the south slope of the mountain near Ag. Nelios.
These cracks in the walls of the Protaton church on pictures taken in 1917 could be caused by the earthquake of 1905. On the right the magnificent fresco of John the Forerunner by Panselinos. Both wall paintings are restored now.
Ierissos 1932
The 1932 Ierissos earthquake occurred at 19:20 on 26 September. It caused severe damage in Ierissos and the surrounding part of the Chalkidiki peninsula, with 491 casualties reported.
The Aegean Sea is an area of mainly extensional tectonics caused by the subduction of the African Plate beneath.The earthquake has been attributed to movement on the Stratoni fault, one of the W-E trending faults that shows predominantly dip-slip extension.The earthquake destroyed the town of Ierissos and several villages in the surrounding area.10,000 people were left homeless. The cost of the damage was estimated as 5 million drachmas.
The earthquake was followed by three strong aftershocks (M=6.0, 5.7 & 6.2) in the period 26–29 September, and the largest (M6.3) on 11 May of the following year.
Thessaloniki 1978
The Great Thessaloniki earthquake occurred on 20 June at 23:03 local time. The shock registered 6.2 on the moment magnitude scale, had a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (Violent), and was felt throughout northern Greece, Yugoslavia and Bulgaria. It was the largest event in the area since the 1932 Ierissos earthquake.The epicenter was 20km east of Thessaloniki between lake Koronia and Volvi,in the village of Stivos.It lasted 10 seconds.There was a series of pre-earthquakes with stronger that of size 5.8 degrees on the Richter scale on 25-05-1978 which caused damages on buildings such as the cathedral of Thessaloniki.
It also followed a series of powerful aftershocks with stronger that of 5. degrees on
the Richter scale in 7-05-1978 with epicenter the Lake of Koronia (7,0 - 10,0 km from the town).
49 were dead, 220 were injured,800.000 were left homeless either because their homes were destroyed or because they did not dare to use them.The collapse of a eight-storey building in Hippodrome Square wreaked havoc as 29 were killed out of the total 49 victims.
Moreover,there have been serious damages in historic sites such us Rotonda,the church of Agia sofia and ΠΑΝΑΓΙΑ ΑΧΕΙΡΟΠΟΙΗΤΟΣ
The total cost of repair is estimated 3-5 billion euros.
References