This color-coded map displays a progression of changing global surface temperature anomalies from 1880 through 2015.
Higher than normal temperatures are shown in red and lower then normal termperatures are shown in blue.
The final frame represents the global temperatures 5-year averaged from 2011 through 2015. Scale in degree Celsius.
Climate refers to the long-term regional or even global average of temperature, humidity and rainfall patterns over seasons, years or decades. Climate is global and long-term.
The Earth's climate has changed throughout history. Just in the last 650,000 years there have been seven cycles of glacial advance and retreat, with the adrupt ebd of the last ice age 7,000 years ago marking the beginnung of the modern climate era.
Most of these climate changes are attributed to very small variations in Earth's orbit that change the amount of solar energy our planet receives.
The current warming trend is of particular significance because most of it is very likely human-inducede and proceeding at a rate that is unprecedented in the past 1,300 years-
Climate change refers to a broad range of global phenomena
created predominantly by burning fossil fuels, which add heat-
trapping gases to Earth’s atmosphere.
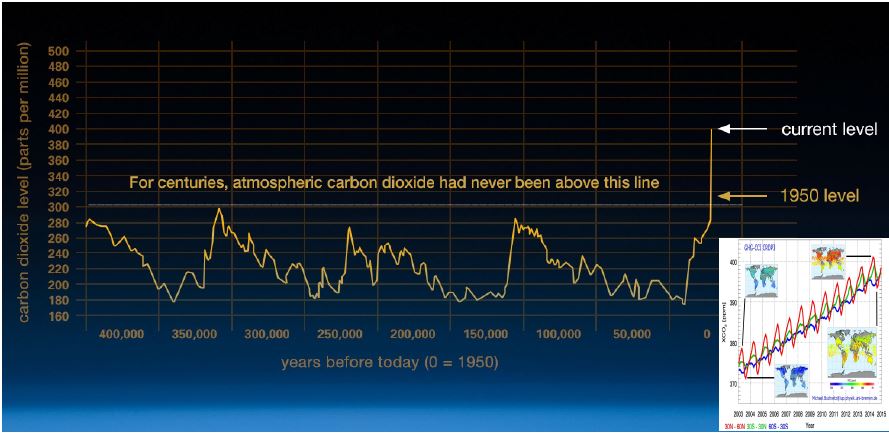
Scientific evidence for warming of the climate system is
unequivocal
Our activities about climate change evidence
 Global warming
Global warming
 Warming oceans
Warming oceans
 Declining Artic sea ice
Declining Artic sea ice
 Glacial retreat
Glacial retreat
 Shrinking ice sheets
Shrinking ice sheets
 Sea level rise
Sea level rise
 Biodiversity loss
Biodiversity loss
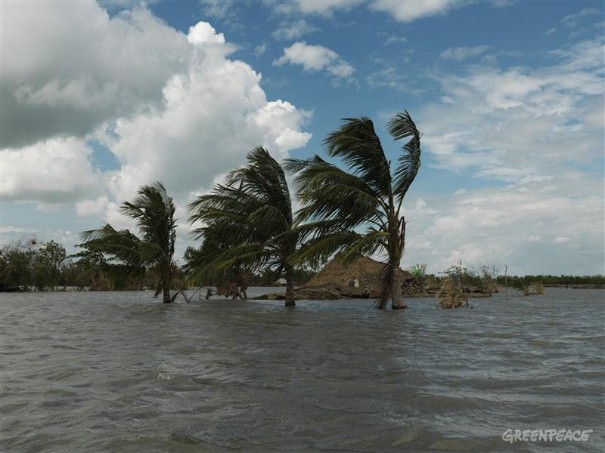 Extreme events
Extreme events