STAR OBSERVATIONS - IDENTIFICATION OF CONSTELLATIONS AND MEASUREMENT OF THE ALTITUDE OF STARS ABOVE THE HORIZON
On the 11th of October 2018, between 19:00 and 20:00, a group of 18 students working in the astronomical group together with the project coordinator conducted observations of the best visible constellations of the night sky in Żyrardów, such as the Great Bear, the Eagle, Cepheus, Cygnus, Lyra, Cassiopeia, Andromeda, Pegasus and the Little Bear. Using a rotary map of the sky, we found them in the sky, identified their characteristic stars, determined in which part of the sky they could be observed, and measured the altitude above the horizon of the brightest of them.

The rotary map of the sky for Poland corresponds to Central European Time (winter time in Poland and the local time for the 15°E meridian). Since on October 11 we have summer time in Poland and the latitude of Żyrardów is 20°26'45″E, we have to subtract an hour from the official time and then add 22 minutes to get the local time in Żyrardów, for which we set the map.

To measure the altitude of stars above the horizon, we used a student astrolabe, which we prepared ourselves, attaching a weight on a thread with adhesive tape in the middle of the long side of a set square with a protractor. The weight is used to determine the vertical direction.
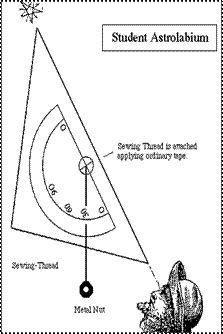
To measure the altitude of a star above the horizon, you must point the long side of the set square towards the star. Then you must hold the thread on the protractor scale and go to an illuminated place to read the angle indicated by the thread. In a bright light you read the angle and write it down. The altitude of the star above the horizon is obtained by subtracting the measured angle from 90o.

The results of our observations are shown in the following presentation:
STAR OBSERVATIONS.pptx