This is the lesson about different kinds of citizenship. Try to write to the Padlet what is your definition of digital citizenship.
DISCUSSIONS IN THE FORUM:
BASIC DEFINITIONS:
Citizenship is the status of a person recognized under the custom or law as being a legal member of a soverereign state. A person may havemultiple citizenships and a person who does not have citizenship of any state is said to be stateless.Nationality is often used as a synonym for citizenship – in interanational law – although the term is sometimes understood as denoting a person's membership of a nation. In some countries, e.g. the USA, the UK, nationality and citizenship can have different meanings.
Active citizenship is the philosophy that citizens should work towards the betterment of their community through economic participation, public, volunteer work, and other such efforts to improve life for all citizens. In this vein, citizenship education is taught in schools, as an academic subject in some countries. By the time children reach secondary education there is an emphasis on such unconventional subjects to be included in academic curriculum. While the diagram on citizenship to the right is rather facile and depth-less, it is simplified to explain the general model of citizenship that is taught to many secondary school pupils. The idea behind this model within education is to instill in young pupils that their actions affect collective citizenship and thus in turn them.
Digital citizenship is the norms of appropriate, responsible technlogy use. Too often we are seeing teenagers or even aduts mususing and abusing technology but not sure what to do. The issue is more what the users do not know but what is considered appropriate technology usage. "A digital citizen accepts and understands the rights and responsibilities of inhabiting ‘cyberspace’, including online safety."
A digital citizen:
· is a confident and capable user of information and communication technology (ICT)
· uses ICTs to participate in educational, cultural, and economic activities
· uses and develops critical thinking skills in cyberspace
· is literate in the language, symbols, and texts of ICTs
· is aware of ICT challenges and can manage them effectively
· uses ICT to relate to others in positive, meaningful ways
· demonstrates honesty and integrity and ethical behaviour in their use of ICTs
· respects the concepts of privacy and freedom of speech in a digital world
· contributes and actively promotes the values of digital citizenship
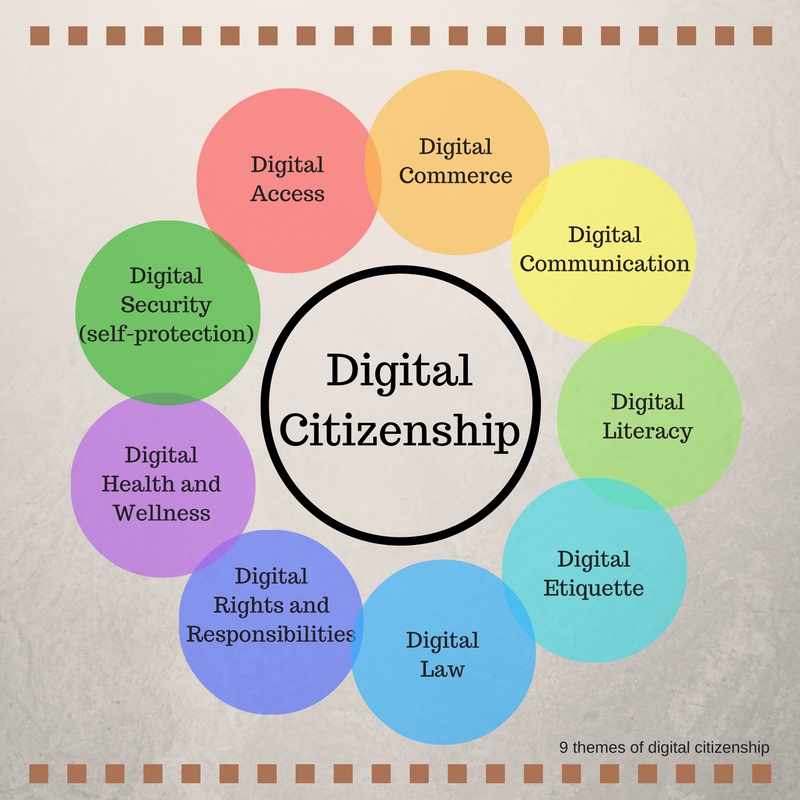
Nine elements of digital citizenship:
· Digital access: full electronic participation in society
· Digital literacy: the process of teaching and learning about ICTs and the use of ICTs
· Digital communication: electronic exchange of information
School environment and student behaviour
· Digital security (self protection): electronic precautions to guarantee safety
· Digital etiquette: electronic standards of conduct or procedure
· Digital rights and responsibilities: those freedoms extended to everyone in a digital world
Student life outside the school environment
· Digital commerce: electronic buying and selling of goods
· Digital heath and wellness: physical and psychological wellbeing in a digital technology world
· Digital law: rights and restrictions
Active digital citizenship is alive form digital citizenship, it leads children, teenagers and adults to become active and informed responsible digital citizens in order to prevent the victimisation of online users, harassment and cyberbullying. We shopuld be active digital citizens in 21st century.