What is the mechanism of the seasons ?
The first thing to know is that the earth's axis is tilted with an angle of 23.5 degrees in relation to its orbital path.
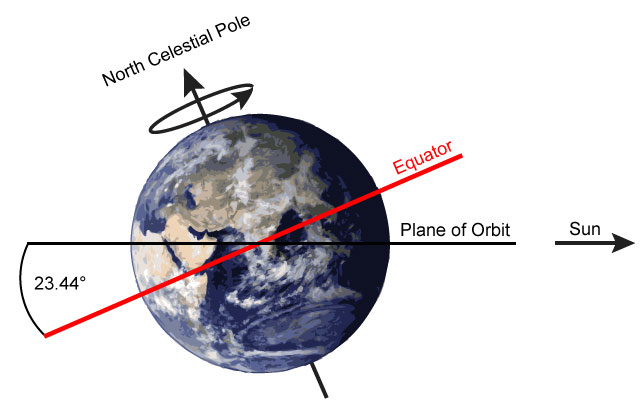
The tilting of the axis resolves in direct sunlight falling on different places during different seasons. This causes variation of the duration of days, nights and seasons.
Thus the seasons are not caused by the distance between the sun and the earth.
But the Earth's tilted rotation affects the Sun's height in the sky to produce two familiar seasonal effects :
-The Sun's height determines how directly the Sun's light ans heat fall on the Earth : the higher the Sun is, the more direct its rays.
-The Sun's height determines the lenght of daylight hours : the higher the Sun is, the longer it remains above the horizon as the Earth rotates.
With sunlight falling more directly on the Earth during the long summer days, the Earth's atmosphere is heated more substantially producing the warm summer temperatures. During the winter months the low Sun altitude results in less direct sunlight and shorter daylight hours during which to heat the atmosphere producing colder temperatures and longer nights.
Solstice

In the summer solstice (June 21), the tilt of the Earth's axis is most inclined toward the Sun. The overhead sun is over of the tropic of Cancer. The Northern hemisphere receive the largest ammount of light. Days got longer light hours on the Northern hemisphere whereas in the Southern hemisphere days got shorter light hours because it receives the shortest ammount of light : it's the winter solstice. The length of the day decreases toward the South pole.
In the winter solstice (December 21), the tilt of the Earth's axis is most inclined away from the Sun. The overhead sun is over the tropic of Capricorn. The Northern hemisphere is in the winter solstice whereas Southern hemisphere is in the summer solstice. The length of the day decreases toward the North pole.

Equinox
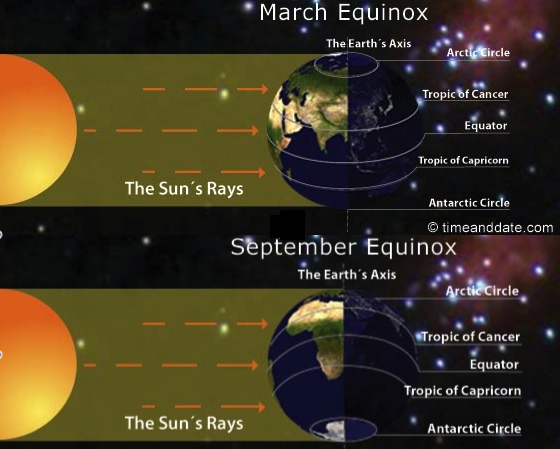
In the Spring equinox (March 21 or 22) the overhead sun is over the equator. The equator receives the largest ammount of solar radiation. At this time the Northern hemisphere is in the spring equinox whereas the Southern hemisphere is in the autumn equinox. On this day the two hemisperes receive a similar ammount of solar raditiation and the length of days and nights is the same at all place in the Earth.
In the Autumn equinox (September 22 or 23) the overhead sun is over the equator again. At this time the Northern hemisphere is in the autumn equinox whereas the Southern hemisphere is in the spring equinox. The length of days and nights is the same at all places in the Earth.
Lattitude
Lattitude is a measure of the distance you are located from the equator. It is commonly shown as an imaginary horizontal line that goes across the earth on maps and is used along with longitude as a reference point to determine location.
The technical definition of latitude is the angular distance north or south from the earth’s equator measured through 90 degrees. Lines of latitude form circles around the earth, with 0 degrees latitude being at the equator and 90° latitude representing the poles.

Latitude is an important factor in determining what type of climate a location will have. For example, we can expect Miami’s climate to be much warmer than that of New York since it is at a lower latitude and is located closer to the equator. Locations at lower latitudes receive stronger and more direct sunlight than locations near the poles. Energy input from the sun is the main driving force in the atmosphere.
Cycle of seasons
