THE SUN
(1) what is the Sun?
(Camille)
Definition : The Sun is the star of the solar system. In the astronomical classification, it is a dwarf star yellow, composed of hydrogen and helium. The Sun is part of the Galaxy called the milky way. Around it orbit the Earth (at the speed of 30 km/s), seven other planets, at least five dwarf planets, very many asteroids and comets and a band of dust. The Sun alone represents 99.86% of the mass of the solar system.

Structure of the Sun :
-The heart of the Sun
Considering that the heart of the Sun extends from the centre to approximately 0.25 solar RADIUS. Its density is greater than 150 000 kg⋅m-3 (150 times the density of water on Earth) and its temperature close to 15 million kelvins (which is in sharp contrast with the surface temperature of the Sun, which is close to the 5 800 kelvins). It is in the heart that occur the nuclear fusion that transform hydrogen into helium in the Sun case. The Sun draws its energy from the nuclear fusion reactions that convert hydrogen to helium in its core. The heart is the only part of the Sun that produce a significant amount of heat Fusion: the rest of the star derives its heat only the energy that comes from. All of the energy that is produced must pass through many successive layers to the photosphere, before escaping into space in the form of solar radiation or particle flux.
-The radiation zone
The radiation area or radiative zone is located approximately between 0.25 and 0.7 solar RADIUS. The solar matter is so hot and so dense that the transfer of heat from the Center to the layers outer is the only thermal radiation.
-The area of convection
The area of convection or convection zone extends from 0.8 solar radius from the centre to the visible surface of the Sun. It is separated from the area of radiation by a thick layer of approximately 3,000 kilometres, the tachocline, which according to recent studies might be the seat of powerful magnetic fields and play an important role in the solar dynamo. In the area of convection material is no longer not dense enough or hot enough to evacuate the heat by radiation: therefore, convection in a vertical motion, the heat is conducted to the photosphere.
-The photosphere
The photosphere is an external part of the star which among other things produces visible light. It is more or less extended: less than 0.1% the RADIUS for dwarf stars, a few hundred kilometres. a few tens of percent of the radius of the star for the most giant, which would give them a hazy outline unlike the Sun at edges.
-The solar corona
The solar corona is the part of the Sun's atmosphere above the chromosphere and spanning several million kilometres by diluting in space

The effects of the Sun on our planet :
The surface of the Earth, the solar radiation includes: 5% of ultra-violet, 40% of visible light and infra-red 55%.
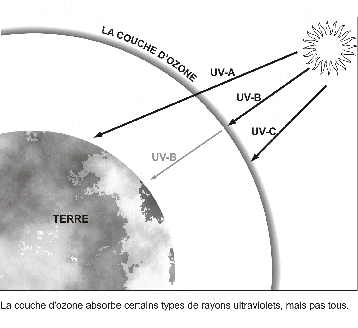
The ultraviolet radiation emitted by the Sun is classified into 3 types of ultraviolet: UV - A having a wavelength of 380 (this value can vary slightly depending on the source) to 315 nanometres (1nm = 1 x 10¯⁹metre), UV - B with the wavelength between 315-280 nm and UV - C which have a wavelength range of 280 to 200 nm. However only UV - A and a small part of the UV - B come up to the surface of the Earth because through the atmosphere all of the UV - C and most of the UV - B are either absorbed, or thoughtful. Thus the solar radiation that we receive includes only 5% of ultraviolet light, these 5% are composed 95% of UV - A and UV - B 5%.
What are the dangers of the sun?
Are there dangers bound to the sun? What are the dangers of the sun?
DOCUMENT 1:

This document represents the photography of the back of a man having got sunburned.
A sunburn is an inflammation of the skin showing itself by a rednessof the skin, the pains, the itches and possibly the blisters.
As we can notice it, the skin is burned because of a too strong sun exposure, the skin was not enough protected.
It is necessary to pay attention, a simple sunburn not been looked after to pull graver consequences on the skin, it is necessary to put thus at once some cream on the burn during several days.
DOCUMENT 2:

This document is a photography of the back of a woman. Thanks to this photography, we are going to be able to discover one of the dangers of the sun.
We can see that the skin "peeled", because of a too long exhibition in the sun. We can suspect as well as she(it) did not enough protect the skin, she(it) should have put a more effective sunscreen, or recover regularly from some cream during day.
The skin peeled after a sunburn.
This phenomenon indicates the loss of the superficial coats of the skin in the form of scraps of skin. The skin is thus even more vulnerable than it was it previously.
DOCUMENT 3:
